用相机拍照
现在是有趣的部分 - 添加使用 Capacitor 相机接口 使用设备相机拍照的功能。我们将从为网络构建它开始,然后进行一些小调整以使其在移动设备(iOS 和 Android)上运行。
¥Now for the fun part - adding the ability to take photos with the device’s camera using the Capacitor Camera API. We’ll begin with building it for the web, then make some small tweaks to make it work on mobile (iOS and Android).
为此,我们将创建自己的自定义 React 钩子来管理图库的照片。
¥To do so, we will create our own custom React hook that will manage the photos for the gallery.
如果你不熟悉 React Hooks,React 官方文档中的 介绍 React Hooks 是一个很好的入门资源。
¥If you are not familiar with React Hooks, Introducing React Hooks from the official React docs is a good resource to start with.
在 src/hooks/usePhotoGallery.ts 创建一个新文件并打开它。
¥Create a new file at src/hooks/usePhotoGallery.ts and open it up.
自定义钩子只是使用其他 React 钩子的函数。这就是我们要做的!我们将首先从 React 核心、Ionic React Hooks 项目和 Capacitor 导入我们将要使用的各种钩子和实用程序:
¥A custom hook is just a function that uses other React hooks. And that's what we will be doing! We will start by importing the various hooks and utilities we will be using from React core, the Ionic React Hooks project, and Capacitor:
import { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import { isPlatform } from '@ionic/react';
import { Camera, CameraResultType, CameraSource, Photo } from '@capacitor/camera';
import { Filesystem, Directory } from '@capacitor/filesystem';
import { Preferences } from '@capacitor/preferences';
import { Capacitor } from '@capacitor/core';
接下来,创建一个名为 usePhotoGallery 的函数:
¥Next, create a function named usePhotoGallery:
export function usePhotoGallery() {
const takePhoto = async () => {
const photo = await Camera.getPhoto({
resultType: CameraResultType.Uri,
source: CameraSource.Camera,
quality: 100,
});
};
return {
takePhoto,
};
}
我们的 usePhotoGallery 钩子公开了一个名为 takePhoto 的方法,该方法又调用 Capacitor 的 getPhoto 方法。
¥Our usePhotoGallery hook exposes a method called takePhoto, which in turn calls into Capacitor's getPhoto method.
注意这里的魔力:没有特定于平台的代码(Web、iOS 或 Android)!Capacitor Camera 插件为我们抽象了这一点,只留下一个方法调用 - getPhoto() - 这将打开设备的相机并允许我们拍照。
¥Notice the magic here: there's no platform-specific code (web, iOS, or Android)! The Capacitor Camera plugin abstracts that away for us, leaving just one method call - getPhoto() - that will open up the device's camera and allow us to take photos.
我们需要采取的最后一步是使用 Tab2 页面中的新钩子。返回 Tab2.tsx 并导入钩子:
¥The last step we need to take is to use the new hook from the Tab2 page. Go back to Tab2.tsx and import the hook:
import { usePhotoGallery } from '../hooks/usePhotoGallery';
在函数组件中的 return 语句之前,使用钩子访问 takePhoto 方法:
¥And right before the return statement in the functional component, get access to the takePhoto method by using the hook:
const Tab2: React.FC = () => {
const { takePhoto } = usePhotoGallery();
// snip - rest of code
保存文件,如果尚未保存,请通过运行 ionic serve 在浏览器中重新启动开发服务器。在照片库选项卡上,单击相机按钮。如果你的计算机有任何类型的网络摄像头,则会出现一个模式窗口。来张自拍照吧!
¥Save the file, and if you’re not already, restart the development server in your browser by running ionic serve. On the Photo Gallery tab, click the Camera button. If your computer has a webcam of any sort, a modal window appears. Take a selfie!
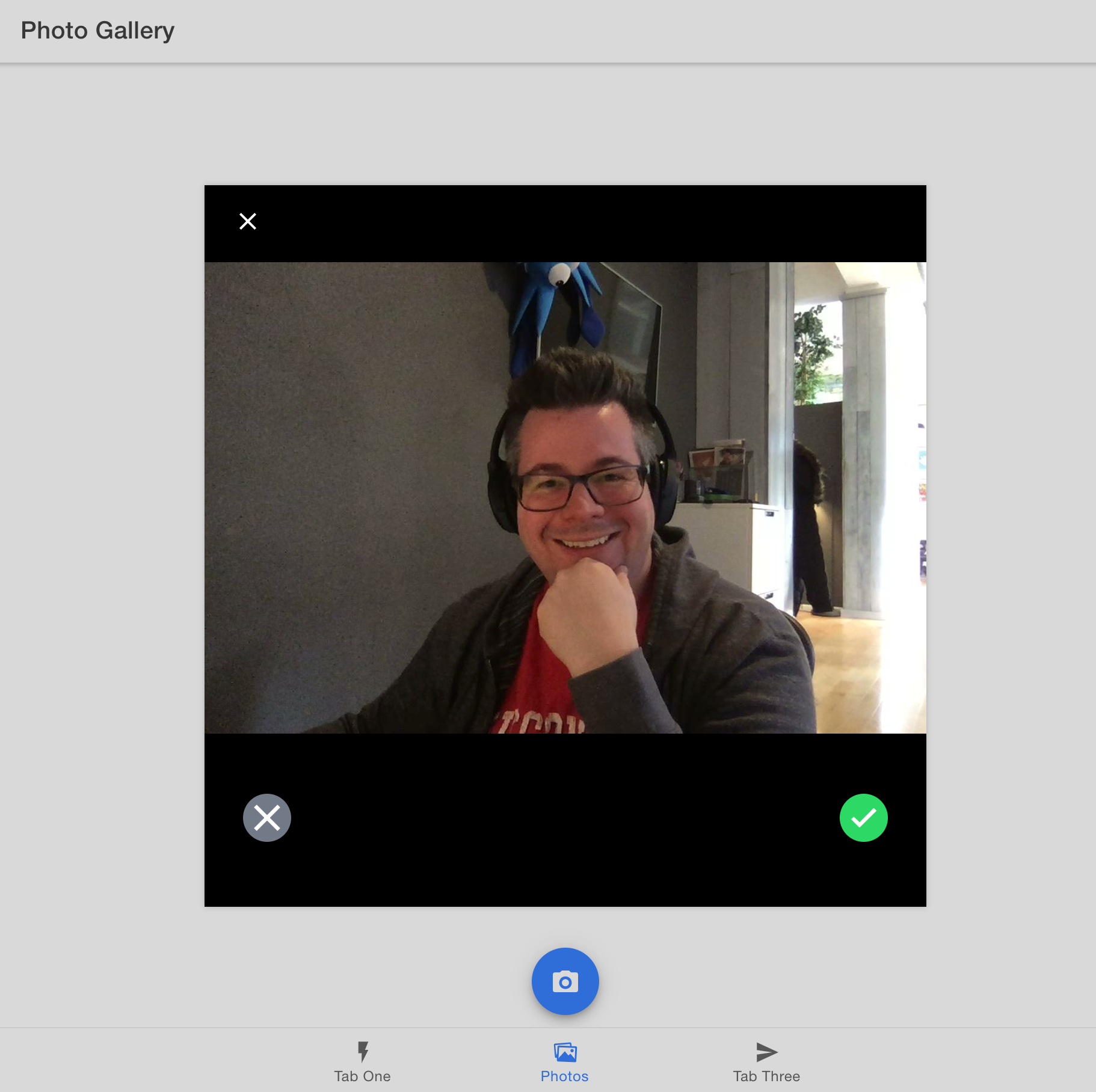
(你的自拍可能比我的好得多)
¥*(Your selfie is probably much better than mine)*
拍完照片后,它就消失了。我们仍然需要在我们的应用中显示它并保存它以供将来访问。
¥After taking a photo, it disappears. We still need to display it within our app and save it for future access.
显示照片
¥Displaying Photos
首先,我们将创建一个新类型来定义我们的照片,它将保存特定的元数据。将以下 UserPhoto 接口添加到 usePhotoGallery.ts 文件中主函数之外的某个位置:
¥First we will create a new type to define our Photo, which will hold specific metadata. Add the following UserPhoto interface to the usePhotoGallery.ts file, somewhere outside of the main function:
export interface UserPhoto {
filepath: string;
webviewPath?: string;
}
回到函数的顶部(在调用 usePhotoGallery 之后,我们将定义一个状态变量来存储用相机拍摄的每张照片的数组。
¥Back at the top of the function (right after the call to usePhotoGallery, we will define a state variable to store the array of each photo captured with the Camera.
const [photos, setPhotos] = useState<UserPhoto[]>([]);
当相机完成拍��照后,从 Capacitor 返回的结果照片将存储在 photo 变量中。我们想要创建一个新的照片对象并将其添加到照片状态数组中。我们确保不会通过创建新数组来意外改变当前照片数组,然后调用 setPhotos 将数组存储到状态中。更新 takePhoto 方法并在 getPhoto 调用后添加以下代码:
¥When the camera is done taking a picture, the resulting Photo returned from Capacitor will be stored in the photo variable. We want to create a new photo object and add it to the photos state array. We make sure we don't accidentally mutate the current photos array by making a new array, and then call setPhotos to store the array into state. Update the takePhoto method and add this code after the getPhoto call:
const fileName = Date.now() + '.jpeg';
const newPhotos = [
{
filepath: fileName,
webviewPath: photo.webPath,
},
...photos,
];
setPhotos(newPhotos);
接下来,让我们从钩子中公开照片数组。更新返回声明以包含照片:
¥Next, let's expose the photos array from our hook. Update the return statement to include the photos:
return {
photos,
takePhoto,
};
返回 Tab2 组件,访问照片:
¥And back in the Tab2 component, get access to the photos:
const { photos, takePhoto } = usePhotoGallery();
将照片存储到主数组中后,我们可以在屏幕上显示图片。添加 网格组件,以便在将照片添加到图库时每张照片都能很好地显示,并循环遍历照片数组中的每张照片,为每张照片添加一个图片组件 (<IonImg>)。将 src(源)指向照片的路径:
¥With the photo(s) stored into the main array we can display the images on the screen. Add a Grid component so that each photo will display nicely as photos are added to the gallery, and loop through each photo in the Photos array, adding an Image component (<IonImg>) for each. Point the src (source) to the photo’s path:
<IonContent>
<IonGrid>
<IonRow>
{photos.map((photo, index) => (
<IonCol size="6" key={photo.filepath}>
<IonImg src={photo.webviewPath} />
</IonCol>
))}
</IonRow>
</IonGrid>
<!-- <IonFab> markup -->
</IonContent>
保存所有文件。在网络浏览器中,单击相机按钮并拍摄另一张照片。这次,照片显示在照片库中!
¥Save all files. Within the web browser, click the Camera button and take another photo. This time, the photo is displayed in the Photo Gallery!
接下来,我们将添加对将照片保存到文件系统的支持,以便稍后可以在我们的应用中检索和显示它们。
¥Up next, we’ll add support for saving the photos to the filesystem, so they can be retrieved and displayed in our app at a later time.