Ionic React 快速入门简介
什么是 Ionic 框架?
¥What is Ionic Framework?
首先,如果你是新来的,欢迎!Ionic 是一个免费的开源组件库,用于构建在 iOS、Android、Electron 和 Web 上运行的应用。你可以使用熟悉的技术(HTML、CSS、JavaScript)编写一次应用并部署到任何平台。
¥First off, if you're new here, welcome! Ionic is a free and open source component library for building apps that run on iOS, Android, Electron, and the Web. You write your app once using familiar technologies (HTML, CSS, JavaScript) and deploy to any platform.
除了 UI 组件之外,Ionic 还提供了一个命令行工具,用于创建新应用以及部署到我们支持的各种平台。
¥Along with the UI components, Ionic also provides a command line tool for creating new apps, as well as deploying to the various platforms we support.
在本指南中,我们将介绍 React 和 Ionic 的基础知识,包括任何 Ionic 特定功能。如果你熟悉 React,请享受本指南并了解有关 Ionic 的新知识。如果你对其中任何一个都不熟悉,不用担心!本指南将涵盖基础知识并提供足够的信息来启动和运行应用。
¥In this guide, we'll go over the basics of both React and Ionic, including any Ionic specific features. If you're familiar with React, enjoy the guide and learn something new about Ionic. If you're not familiar with either, no worries! This guide will cover the basics and provide enough information to get an app up and running.
使用 Ionic CLI 创建项目
¥Creating a project with the Ionic CLI
首先,让我们安装最新版本的 Ionic CLI。
¥To get started, let's install the latest version of the Ionic CLI.
npm install -g @ionic/cli
从这里开始,全局命令 ionic 将允许使用 Ionic 和任何其他依赖创建 React 项目。要创建新项目,请运行以下命令:
¥From here, the global command ionic will allow for the creation of a React project with Ionic and any other dependencies. To create a new project, run the following command:
ionic start myApp blank --type=react
cd myApp
从这里,我们运行 ionic serve 并让我们的项目在浏览器中运行。
¥From here, we run ionic serve and have our project running in the browser.
看看 React 组件
¥A look at a React Component
我们应用的基础将位于 src 目录中,主入口点将是我们的 index.tsx。如果我们在代码编辑器中打开项目并打开 src/index.tsx,我们应该看到以下内容:
¥The base of our app will be in the src directory, and the main entry point will be our index.tsx. If we open our project in a code editor and open src/index.tsx, we should see the following:
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import App from './App';
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('root'));
那么这是怎么回事呢?嗯,前三行引入了一些依赖。第一个是 React 本身。这使我们能够使用类似 HTML 的语法(称为 JSX)编写组件。稍后我们将讨论 JSX。
¥So what's going on here? Well, the first three lines are pulling in some dependencies. The first being React itself. This allows us to write components in an HTML-like syntax called JSX. We'll talk about JSX a bit later on.
第二个导入是针对 ReactDOM 的。ReactDOM.render 方法是浏览器/DOM 特定的方法,用于获取我们的组件并将其渲染到指定的 DOM 节点。
¥The second import is for ReactDOM. The ReactDOM.render method is the browser/DOM specific way of taking our components and rendering it to a specified DOM node.
最后导入的是我们应用的根组件,简单地命名为 App。这是我们的第一个 React 组件,将在 React 应用的引导过程中使用。
¥The last import is the root component for our app, simply named App. This is our first React component and will be used in the bootstrapping process for our React app.
如果我们打开 App.tsx,我们应该看到以下内容。
¥If we open App.tsx, we should see the following.
import React from 'react';
import { Route } from 'react-router-dom';
import { IonApp, IonRouterOutlet } from '@ionic/react';
import { IonReactRouter } from '@ionic/react-router';
import Home from './pages/Home';
/* Core CSS required for Ionic components to work properly */
import '@ionic/react/css/core.css';
const App: React.FC = () => (
<IonApp>
<IonReactRouter>
<IonRouterOutlet>
<Route path="/home" component={Home} exact={true} />
<Route exact path="/" render={() => <Redirect to="/home" />} />
</IonRouterOutlet>
</IonReactRouter>
</IonApp>
);
乍一看,似乎发生了很多事情,所以让我们从第一组导入开始进行分解。
¥At first glance, it may look like a lot is going on, so let's break it down, starting with the first group of imports.
import React from 'react';
import { Route } from 'react-router-dom';
import { IonApp, IonRouterOutlet } from '@ionic/react';
import { IonReactRouter } from '@ionic/react-router';
import Home from './pages/Home';
与 index.tsx 类似,我们首先必须导入 React 才能使用 JSX。
¥Similar to index.tsx, we first must import React to use JSX.
下一次导入来自 react-router-dom。我们正在导入 Route,这就是我们将应用的 URL 与我们想要渲染的组件相匹配的方式
¥The next import is from react-router-dom. We're importing Route, which is how we’ll match the app’s URL with the components we want to render
继 ReactRouter 之后,我们接下来首次导入 Ionic。要在 React 中使用组件,必须首先导入它。因此,对于 Ionic 来说,这意味着任何时候我们想要使用 Button 或 Card 时,都必须将其添加到我们的导入中。对于我们的应用组件,我们仅使用 IonApp、IonRouterOutlet 和 IonReactRouter。
¥Following ReactRouter, we next have our first imports for Ionic. To use a component in React, you must first import it. So for Ionic, this means anytime we want to use a Button or a Card, it must be added to our imports. In the case of our App component, we're only using IonApp, IonRouterOutlet, and IonReactRouter.
IonReactRouter 是一个封装 ReactRouter 的 BrowserRouter 组件的组件。它的行为或多或少与 BrowserRouter 相同,但有一些差异。我们有一个更深入的指南来讨论 React 导航文档 中的这些差异。
¥IonReactRouter is a component that wraps ReactRouter’s BrowserRouter component. It more or less behaves the same as BrowserRouter with a few differences. We have a deeper guide that goes over these differences in our React Navigation Docs.
最后一个重要的导入是 Home 组件导入。这是我们能够在应用中导航到的组件。稍后我们将讨论导航部分。
¥The last important import is the Home component import. This is a component that we will be able to navigate to in our app. We'll look at the navigation part a bit later.
CSS 导入从 Ionic 中引入实用样式,例如填充、排版等。
¥The CSS import is pulling in the utility styles from Ionic for things like padding, typography, etc.
在检查了所有导入之后,我们现在首先看一下 React 组件:
¥After reviewing all of the imports, we now get to our first look at a React Component:
const App: React.FC = () => (
<IonApp>
<IonReactRouter>
<IonRouterOutlet>
<Route path="/home" component={Home} exact={true} />
<Route exact path="/" render={() => <Redirect to="/home" />} />
</IonRouterOutlet>
</IonReactRouter>
</IonApp>
);
该 React 组件为我们的应用设置初始路由,并包含一些用于动画和布局的核心 Ionic 组件(IonRouterOutlet 和 IonApp)。值得注意的一件事是,在 React 中,为了进行数据绑定,值在大括号 ({}) 中传递。因此,在 Route 组件中,我们可以将 component 的值设置为之前的 Home 组件。这就是 React 知道该值不是字符串,而是对组件的引用的方式。
¥This React component sets up the initial routing for our app, as well as include some core Ionic components for animations and layout (IonRouterOutlet and IonApp). One thing that stands out is that in React, to do data-binding, the value is passed in curly braces ({}). So in the Route component, we can set the value of component to the Home component from earlier. This is how React will know that that value is not a string, but a reference to a component.
这里需要注意的是,这些都是标准的 React DOM 库,这意味着没有自定义集成层或转译步骤。
¥What's important to note here is that these are all standard React DOM libraries, meaning there's no custom integration layer or transpilation step.
使用样式的组件
¥A component with style
现在 App 确实没有太多需要修改的地方。这是容器组件的基本示例。设置了 Router 逻辑后,它所负责的就是渲染与给定 URL 路由匹配的组件。由于我们已经有了一个组件/路由设置,因此让我们继续修改 Home 组件。
¥Now the App does not really have a lot to modify here. It's a basic example of a container component. With the Router logic set, all it's responsible for is to render a component that matches the given URL route. Since we already have one component/router setup, let's go ahead and modify our Home component.
目前,Home 组件如下所示:
¥Currently, the Home component looks like so:
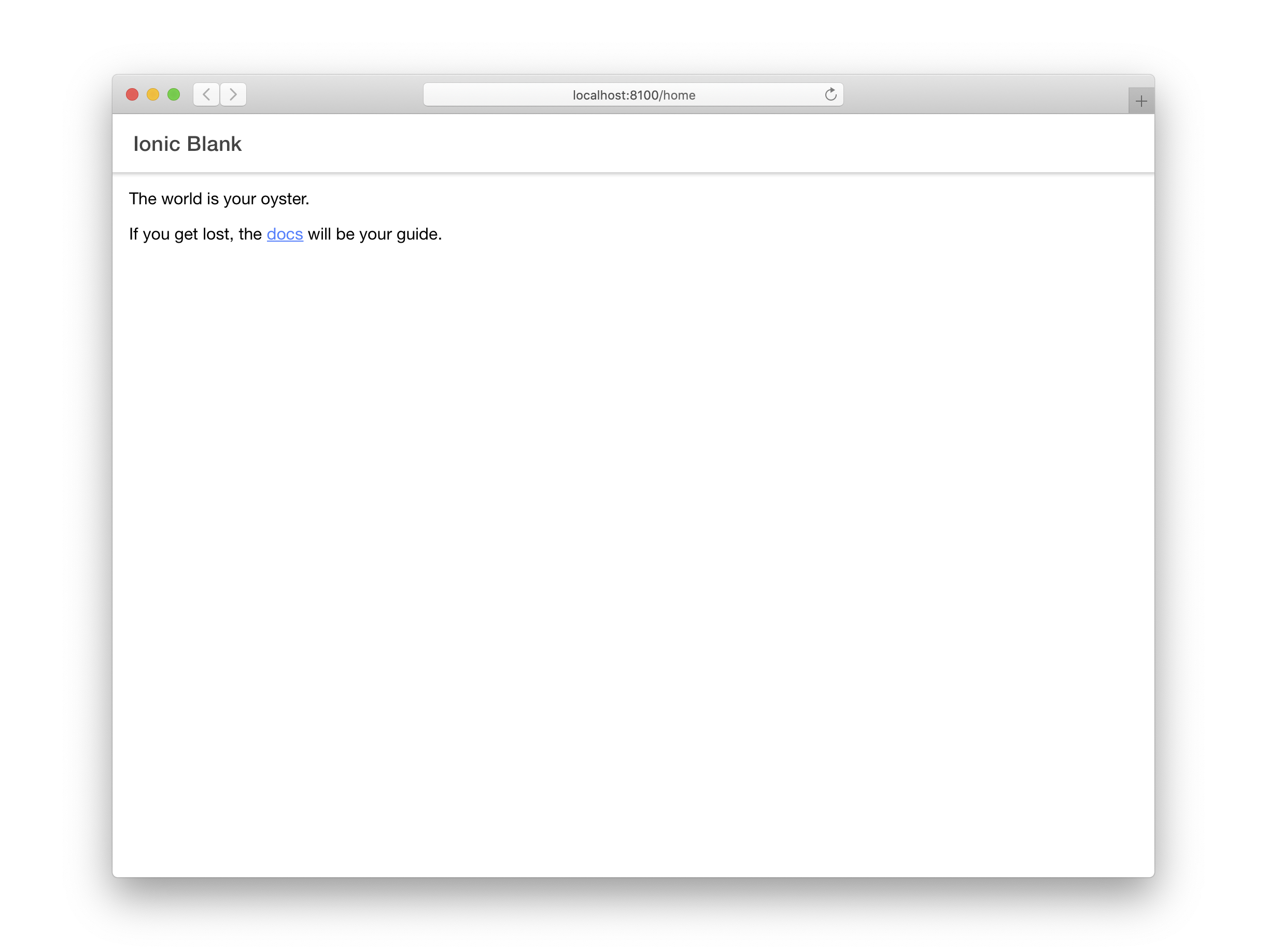
import { IonContent, IonHeader, IonPage, IonTitle, IonToolbar } from '@ionic/react';
import React from 'react';
const Home: React.FC = () => {
return (
<IonPage>
<IonHeader>
<IonToolbar>
<IonTitle>Ionic Blank</IonTitle>
</IonToolbar>
</IonHeader>
<IonContent className="ion-padding">
The world is your oyster.
<p>
If you get lost, the{' '}
<a target="_blank" rel="noopener" href="https://ionic.nodejs.cn/">
docs
</a>{' '}
will be your guide.
</p>
</IonContent>
</IonPage>
);
};
就像我们开始使用的 App 组件一样,我们有一些特定 Ionic 组件的导入,React 的导入,然后是我们的 React 组件本身。
¥Much like the App component we started with, we have some imports for specific Ionic components, an import for React, and then our React component itself.
IonPage 是所有页面的基础组件(具有路由/URL 的组件),并包括全屏组件的一些常见构建块,如标题、标题和内容组件。
¥IonPage is the base component for all pages (a component with a route/URL), and includes some common building blocks of a full-screen component, like header, title, and content components.
创建你自己的页面时,不要忘记让 IonPage 作为它们的根组件。让 IonPage 作为根组件很重要,因为它有助于确保转换正常工作并提供 Ionic 组件所依赖的基础 CSS。
¥When creating your own pages, don't forget to have IonPage be the root component for them. Having IonPage be the root component is important because it helps ensure transitions work properly as well as provides the base CSS the Ionic components rely on.
IonHeader 有点不言自明。它是一个应该存在于页面顶部的组件。除了处理一些基于 Flexbox 的布局之外,IonHeader 本身并没有做太多事情。它用于容纳其他组件,例如 IonToolbar 或 IonSearchbar。
¥IonHeader is a bit self explanatory. It's a component that is meant to exist at the top of the page. IonHeader itself doesn't do much by itself, aside from handling some flexbox-based layout. It's meant to hold other components, like IonToolbar or IonSearchbar.
IonContent,顾名思义,是我们页面的主要内容区域。它负责提供用户将与之交互的可滚动内容,以及可在应用中使用的任何滚动事件。
¥IonContent is, as its name suggests, the main content area for our page. It's responsible for providing the scrollable content that users will interact with, plus any scroll events that could be used in an app.
我们当前的内容相对简单,但不包含任何可以在真实应用中使用的内容,所以让我们改变一下。
¥Our current content is relatively simple but does not contain anything that could be used in a real app, so let's change that.
为了简洁起见,我们排除了组件的重复部分,例如其他组件的函数声明或导入语句。
¥For brevity, we're excluding repeating parts of our component, like the function declaration or import statements for other components.
<IonPage>
...
<IonContent>
<IonList>
<IonItem>
<IonCheckbox labelPlacement="end" justify="start">
<h1>Create Idea</h1>
<IonNote>Run Idea by Brandy</IonNote>
</IonCheckbox>
<IonBadge color="success" slot="end">
5 Days
</IonBadge>
</IonItem>
</IonList>
</IonContent>
</IonPage>
在 IonContent 中,我们添加了 IonList 和更复杂的 IonItem 组件。让我们看看 IonItem,因为它是这里的核心。
¥Here in our IonContent, we're adding an IonList and a much more involved IonItem component. Let's look at IonItem, as it's the centerpiece here.
<IonItem>
<IonCheckbox labelPlacement="end" justify="start">
<h1>Create Idea</h1>
<IonNote>Run Idea by Brandy</IonNote>
</IonCheckbox>
<IonBadge color="success" slot="end">
5 Days
</IonBadge>
</IonItem>
查看我们的代码,我们有一个名为 slot 的特殊属性。这是让 IonItem 知道渲染时将 IonBadge 放置在何处的关键�。这不是一个 React API,而是一个 Web 标准 API,并且在许多 Ionic Framework 组件中使用。(有关插槽的更多信息,请参阅此处的 MDN 文档。)
¥Looking at our code, we have a special attribute called slot. This is key for letting the IonItem know where to place the IonBadge when it renders. This is not a React API, but a web standards API, and it is used in many Ionic Framework components. (For more information on slots, see the MDN docs here.)
让我们看看 Ionic 的另一个组件 FAB。浮动操作按钮是提供从应用的其余部分提升的主要操作的好方法。对于这个 FAB,我们需要三个组件:一个 FAB、一个 FAB 按钮和一个图标。
¥Let's look at another component from Ionic, FAB. Floating Action Buttons are a nice way to provide a main action that is elevated from the rest of an app. For this FAB, we'll need three components: a FAB, a FAB Button, and an Icon.
import { add } from ‘ionicons/icons’;
…
<IonContent>
<IonList>
...
</IonList>
<IonFab vertical="bottom" horizontal="end" slot="fixed">
<IonFabButton>
<IonIcon icon={add} />
</IonFabButton>
</IonFab>
</IonContent>
在我们的主 IonFab 上,我们使用垂直和水平属性设置其位置。我们还使用 slot 属性将渲染位置设置为 "fixed"。这将告诉 IonFab 在 IonContent 中的可滚动内容之外进行渲染。
¥On our main IonFab, we're setting its positioning with the vertical and horizontal attributes. We're also setting the render location to "fixed" with the slot attribute. This will tell IonFab to render outside of the scrollable content in IonContent.
现在让我们为此连接一个点击处理程序。我们想要做的是,当我们单击按钮时,我们将导航到一个新页面(我们稍后将创建该页面)。为此,我们需要访问 React Router 的 useHistory hook API。值得庆幸的是,useHistory 钩子使这一切变得容易,因为它可以从 react-router 包中导入。
¥Now let's wire up a click handler to this. What we want to do is when we click the button, we'll navigate to a new page (which we'll create in a moment). To do this, we'll need to get access to React Router's useHistory hook API. Thankfully the useHistory hook makes this easy since it can be imported from the react-router package.
import { add } from 'ionicons/icons';
import { useHistory } from 'react-router';
...
const Home: React.FC<RouteComponentProps> = () => {
const history = useHistory();
return (
<IonPage>
<IonHeader>...</IonHeader>
<IonContent>
<IonList>...</IonList>
<IonFab vertical="bottom" horizontal="end" slot="fixed">
<IonFabButton onClick={() => history.push('/new')}>
<IonIcon icon={add} />
</IonFabButton>
</IonFab>
</IonContent>
</IonPage>
);
}
export default Home;
在我们的组件声明中,我们传入 props,其类型为 RouteComponentProps(从 react-router 导入)。这个 props 对象使我们能够访问 React Router 的历史 API,从而允许我们将新路由推送到导航堆栈上。在我们的 IonFabButton 上,我们可以添加一个点击处理程序,只需调用 props.history.push 并传入新路由即可。在本例中,我们将导航到 new。
¥In our component declaration, we're passing in props which is of type RouteComponentProps (imported from react-router). This props object gives us access to the history API from React Router, allowing us to push a new route onto the navigation stack. On our IonFabButton, we can add a click handler, and just call props.history.push and pass in the new route. In this case, we'll navigate to new.
<IonFabButton onClick={() => props.history.push('/new')} >
创建新路由
¥Creating a new Route
现在我们已经有了在应用中导航的部件,我们需要创建一个新组件并将新路由添加到我们的路由声明中。让我们打开 App.tsx 文件并添加新路由。
¥Now that we have the pieces in place to navigate in our app, we need to create a new component and add the new route to our router declaration. Let's open our App.tsx file and add the new route.
...
import Home from './pages/Home';
import NewItem from './pages/NewItem';
...
const App: React.FC = () => {
const isAuthed = true;
return (
<IonApp>
<IonReactRouter>
<IonRouterOutlet>
<Route path="/home" component={Home} />
<Route path="/new" component={NewItem} />
<Redirect exact from="/" to="/home" />
</IonRouterOutlet>
</IonReactRouter>
</IonApp>
);
}
export default App;
现在我们的路由有了路由 /new 的条目,我们将创建所需的组件 NewItem。这将存在于 src/pages/NewItem.tsx
¥With our router now having an entry for the route /new, we'll create the component needed, NewItem. This will exist in src/pages/NewItem.tsx
现在让我们用一些占位符内容填充 NewItem.tsx。
¥Let's fill the NewItem.tsx with some placeholder content for the moment.
import { IonBackButton, IonButtons, IonContent, IonHeader, IonPage, IonTitle, IonToolbar } from '@ionic/react';
import React from 'react';
const NewItem: React.FC = () => {
return (
<IonPage>
<IonHeader>
<IonToolbar>
<IonButtons slot="start">
<IonBackButton />
</IonButtons>
<IonTitle>New Item</IonTitle>
</IonToolbar>
</IonHeader>
<IonContent></IonContent>
</IonPage>
);
};
export default NewItem;
每个视图必须包含 IonPage 组件。如果没有它,页面转换将无法正常工作。请参阅 IonPage 文档 了解更多信息。
¥Each view must contain an IonPage component. Page transitions will not work correctly without it. See the IonPage Documentation for more information.
这里的内容非常简单,看起来应该与 Home 组件类似。新的是 IonBackButton 组件。这用于导航回之前的路由。很直接吗?好的,但是如果我��们重新加载页面怎么办?
¥The content here is pretty straight forward and should look similar to the Home component. What is new is the IonBackButton component. This is used to navigate back to the previous route. Pretty straight forward? Ok, but what if we reload the page?
好吧,在这种情况下,内存中的历史记录丢失了,因此后退按钮消失了。为了解决这个问题,我们可以将 defaultHref 属性值设置为没有历史记录时要导航到的 URL。
¥Well, in this case, the in-memory history is lost, so the back button disappears. To address this, we can set the defaultHref attribute value to the URL we want to navigate to if there is no history.
return (
<IonPage>
<IonHeader>
<IonToolbar>
<IonButtons slot="start">
<IonBackButton defaultHref="/home" />
</IonButtons>
<IonTitle>New Item</IonTitle>
</IonToolbar>
</IonHeader>
<IonContent />
</IonPage>
);
在这里,当我们重新加载时,如果不存在应用历史记录,我们将能够导航回我们的主页路由。
¥Here, when we reload, if there is no app history present, we'll be able to navigate back to our home route.
添加图标
¥Adding Icons
Ionic React 预装了 (https://ionic.io/ionicons/)。你需要做的就是从 ionicons 包中导入你选择的图标,然后通过 icon 属性将其传递给 IonIcon 组件:
¥Ionic React comes with (https://ionic.io/ionicons/) pre-installed. All you need to do is import the icon of your choice from the ionicons package, and pass it to an IonIcon component through the icon prop:
import React from 'react';
import { IonButton, IonContent, IonIcon } from '@ionic/react';
import { camera } from 'ionicons/icons';
export const IconExample: React.FC = () => {
<IonContent>
<IonButton>
<IonIcon icon={camera} />
Take Picture
</IonButton>
</IonContent>;
};
请注意,对于 React,我们传递导入的 SVG 引用,而不是作为字符串的图标名称。
¥Note that for React, we are passing the imported SVG reference, not the icon name as a string.
开发者还可以根据模式设置不同的图标:
¥Developers also have the option of setting different icons based upon the mode:
import React from 'react';
import { IonButton, IonContent, IonIcon } from '@ionic/react';
import { logoAndroid, logoApple } from 'ionicons/icons';
export const IconExample: React.FC = () => {
<IonContent>
<IonButton>
<IonIcon ios={logoApple} md={logoAndroid} />
</IonButton>
</IonContent>;
};
构建原生应用
¥Build a Native App
我们现在已经掌握了 Ionic React 应用的基础知识,包括一些 UI 组件和导航。Ionic 组件的很棒之处在于它们可以在任何地方工作,包括 iOS、Android 和 PWA。为了部署到移动设备及其他设备,我们使用 Ionic 的跨平台应用运行时 Capacitor。它提供了一组一致的、以 Web 为中心的 API,使应用能够尽可能接近 Web 标准,同时在支持它们��的平台上访问丰富的原生设备功能。
¥We now have the basics of an Ionic React app down, including some UI components and navigation. The great thing about Ionic’s components is that they work anywhere, including iOS, Android, and PWAs. To deploy to mobile and beyond, we use Ionic’s cross-platform app runtime Capacitor. It provides a consistent, web-focused set of APIs that enable an app to stay as close to web-standards as possible while accessing rich native device features on platforms that support them.
添加原生功能很容易。首先,将 Capacitor 添加到你的项目中:
¥Adding native functionality is easy. First, add Capacitor to your project:
ionic integrations enable capacitor
接下来,构建项目,然后添加你选择的平台:
¥Next, build the project, then add your platform of choice:
ionic build
ionic cap add ios
ionic cap add android
我们使用标准的原生 IDE(Xcode 和 Android Studio)来打开、构建和运行 iOS 和 Android 项目:
¥We use the standard native IDEs (Xcode and Android Studio) to open, build, and run the iOS and Android projects:
ionic cap open ios
ionic cap open android
其他详细信息可参见 此处。
¥Additional details can be found here.
接下来,查看可用的 所有 API。有一些很棒的东西,包括 相机接口。我们只需几行代码就可以实现照片拍摄功能:
¥Next, check out all the APIs that are available. There’s some great stuff, including the Camera API. We can implement photo capture functionality in just a few lines of code:
import { IonContent, IonHeader, IonPage, IonTitle, IonToolbar, IonButton } from '@ionic/react';
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import { Plugins, CameraResultType } from '@capacitor/core';
const Home: React.FC = () => {
const { Camera } = Plugins;
const [photo, setPhoto] = useState();
const takePhoto = async () => {
const image = await Camera.getPhoto({
quality: 90,
allowEditing: true,
resultType: CameraResultType.Uri,
});
setPhoto(image.webPath);
};
return (
<IonPage>
<IonHeader>
<IonToolbar>
<IonTitle>Ionic Blank</IonTitle>
</IonToolbar>
</IonHeader>
<IonContent className="ion-padding">
<img src={photo} />
<IonButton onClick={takePhoto}>Take Photo</IonButton>
</IonContent>
</IonPage>
);
};
export default Home;
从这往哪儿走
¥Where to go from here
本指南涵盖了创建 Ionic React 应用的基础知识、添加一些基本导航以及介绍 Capacitor 作为构建原�生应用的一种方式。要更深入地了解如何使用 React 和 Capacitor 构建完整的 Ionic 应用,请关注我们的 第一个应用指南。
¥This guide covered the basics of creating an Ionic React app, adding some basic navigation, and introducing Capacitor as a way of building native apps. To dive deeper into building complete Ionic apps with React and Capacitor, follow our First App guide.
要更详细地了解 Ionic 的组件,请查看 组件 API 页面。有关 React 的更多详细信息,请查看 反应文档。要继续构建原生功能,请参阅 Capacitor 文档。
¥For a more detailed look at Ionic’s components, check out the component API pages. For more details on React, review the React Docs. To keep building native features, see the Capacitor docs.
快乐的应用构建!🎉
¥Happy app building! 🎉